Cryptography
TASK 6
1) What do you mean by cryptography? Explain its real time applications.
Answer:- Cryptography involves creating written or generated codes that allow information to be kept secret. Cryptography converts data into a format that is unreadable for an unauthorized user, allowing it to be transmitted without unauthorized entities decoding it back into a readable format, thus compromising the data.
Symmetric cryptography(secret key encryption) is an encryption system in which the sender and receiver of a message share a single, common key that is used to encrypt and decrypt the message. ... Examples of methods that use symmetric encryption include: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Cryptography is a method of protecting information and communications through the use of codes so that only those for whom the information is intended can read and process it.
Three types of cryptography: secret-key, public key, and hash function. Types of stream ciphers. Feistel cipher. Use of the three cryptographic techniques for secure communication. Kerberos architecture.
Applications of cryptography
Applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, computer passwords, and military communications. Cryptography prior to the modern age was effectively synonymous with encryption, the conversion of information from a readable state to apparent nonsense.
2) Explain classic cryptography with method.
In the classical cryptography the original data i.e., the plain text is transformed into the encoded format i.e. cipher text so that we can transmit this data through insecure communication channels. A data string which known as key is used to control the transformation of the data from plain text to cipher text.
Methods of classical cryptography
Classical Cryptography has two types of techniques:
- Symmetric Cryptography: In the symmetric cryptography a single key is used for encrypting and decryption the data. ...
- Asymmetric Cryptography: In the asymmetric cryptography a pair of key, i.e., public key and private key is used for encryption and decryption.
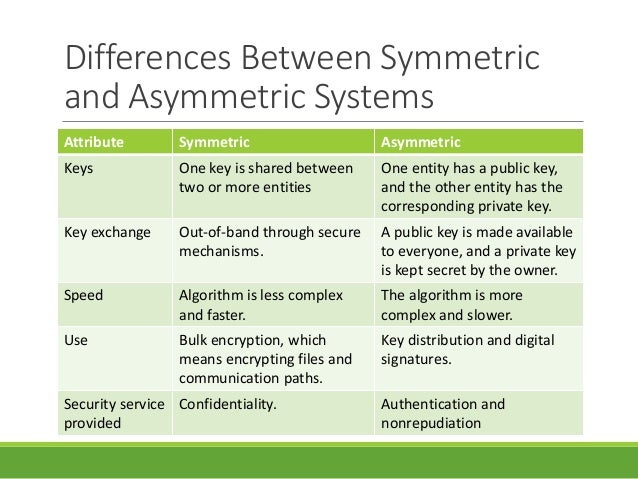
3)Difference between symmetric and asymmetric cryptography.
Symmetric encryption always uses a single key for encryption and decryption of the message. However, in asymmetric encryption, the sender uses the public key for the encryption and private key for decryption. ... On the other hand, Diffie-Hellman and RSA area the most common algorithm used for asymmetric encryption.
4) What the meaning of 192.168.1.2 IP Address?
192.168.0.0 is the beginning of the private IP address range that includes all IP addresses through 192.168.255.255. ... This IP address is used because the router is on the 192.168.1.0 network. In the same way, routers on the 192.168.0.0 network are usually assigned the local, private IP address of 192.168.0.1
The number 28 means the subnet mask off that IP address is 255.255.255.248 meaning this IP address belongs to a subnet of block size 16.
192.168.1.2 is a private IP address. It's often the default IP address for certain models of home broadband routers, typically ones sold outside of the United States. This IP address is also frequently assigned to individual devices within a home network when the router has an IP address of 192.168.1.1.
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. ... Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) defines an IP address as a 32-bit number.
5) When we enter google.com and it loads google page on browser in mentioned procedure where the ip address is used?
You enter a URL into a web browser. The browser looks up the IP address for the domain name via DNS. ... The browser begins rendering the HTML. The browser sends requests for additional objects embedded in HTML (images, css, JavaScript) and repeats steps 3-5.
There are a handful of general steps that occur between the time you request a web page and the time it displays in your browser.
- DNS Lookup.
- Browser sends an HTTP request.
- Server responds and sends back the requested HTML file.
- Browser begins to render HTML.
This is how I would explain it:
- You enter a URL into a web browser
- The browser looks up the IP address for the domain name via DNS
- The browser sends a HTTP request to the server
- The server sends back a HTTP response
- The browser begins rendering the HTML
- The browser sends requests for additional objects embedded in HTML (images, css, JavaScript) and repeats steps 3-5.
- Once the page is loaded, the browser sends further async requests as needed.
Comments
Post a Comment