BASICS OF COMPUTER
COMPUTER WORKSHOP
TASK 1
Q-1 Computer block diagram .
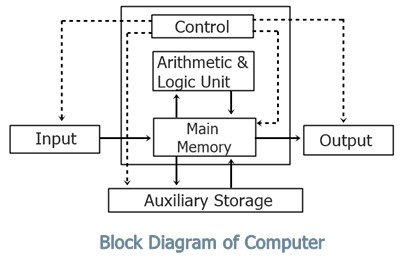
1. Input: This is the process of entering data and programs in to the computer system. You should know that computer is an electronic machine like any other machine which takes as inputs raw data and performs some processing giving out processed data. Therefore, the input unit takes data from us to the computer in an organized manner for processing.
2. Storage: The process of saving data and instructions permanently is known as storage. Data has to be fed into the system before the actual processing starts. It is because the processing speed of Central Processing Unit (CPU) is so fast that the data has to be provided to CPU with the same speed. Therefore the data is first stored in the storage unit for faster access and processing. This storage unit or the primary storage of the computer system is designed to do the above functionality. It provides space for storing data and instructions.
The storage unit performs the following major functions:
• All data and instructions are stored here before and after processing.
• Intermediate results of processing are also stored here.
3. Processing: The task of performing operations like arithmetic and logical operations is called processing. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) takes data and instructions from the storage unit and makes all sorts of calculations based on the instructions given and the type of data provided. It is then sent back to the storage unit.
4. Output: This is the process of producing results from the data for getting useful information. Similarly the output produced by the computer after processing must also be kept somewhere inside the computer before being given to you in human readable form. Again the output is also stored inside the computer for further processing.
5. Control: The manner how instructions are executed and the above operations are performed. Controlling of all operations like input, processing and output are performed by control unit. It takes care of step by step processing of all operations inside the computer.
FUNCTIONAL UNITS
In order to carry out the operations mentioned in the previous section the computer allocates the task between its various functional units. The computer system is divided into three separate units for its operation. They are
Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU)
Logical Unit :After you enter data through the input device it is stored in the primary storage unit. The actual processing of the data and instruction are performed by Arithmetic Logical Unit. The major operations performed by the ALU are addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, logic and comparison. Data is transferred to ALU from storage unit when required. After processing the output is returned back to storage unit for further processing or getting stored.
Control Unit (CU)
The next component of computer is the Control Unit, which acts like the supervisor seeing that things are done in proper fashion. Control Unit is responsible for co coordinating various operations using time signal. The control unit determines the sequence in which computer programs and instructions are executed. Things like processing of programs stored in the main memory, interpretation of the instructions and issuing of signals for other units of the computer to execute them. It also acts as a switch board operator when several users access the computer simultaneously. Thereby it coordinates the activities of computer’s peripheral equipment as they perform the input and output.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The ALU and the CU of a computer system are jointly known as the central processing unit. You may call CPU as the brain of any computer system. It is just like brain that takes all major decisions, makes all sorts of calculations and directs different parts of the computer functions by activating and controlling the operations.


2) Difference between old and new keyboard?
Mechanics and Feel
Electric typewriters used light-touch electrical contacts for keys, easing finger strain. Modern computer keyboards take a very low effort and have little feel; the keys are thin, delicate plastic parts that move little compared to earlier versions.3) Difference between old and new mouse?
The old ball mice were highly mechanical (the ball spun two wheels that rotated slotted discs that blocked and unblocked a li— you know what, it doesn't matter), but the newer mice use an LED or laser reflected off the surface to determine the mouse's movement.
BEST LAPTOP UNDER 60,000/-

Model: VivoBook 15 X512
Model Number: X512
Operating system: Windows 10 Home
Battery Cell: 2
| Brand | Asus |
| Model | VivoBook 15 X512 |
| Release date | 11th June 2019 |
| Model Number | X512 |
| Model Name | VivoBook 15 |
| Series | VivoBook |
| Dimensions (mm) | 230.40 x 357.20 x 19.50 |
| Weight (kg) | 1.6 |
| Operating system | Windows 10 Home |
| Battery Capacity (WHR) | 37 |
| Battery Cell | 2 |
Display
| Size | 15.60-inch |
| Resolution | 1920x1080 pixels |
Processor
| Processor | Intel Core i3 8th Gen 8145U |
Memory
| RAM | 16GB |
Storage
| Hard disk | 1TB |
Inputs
| Web Camera | Yes |
| Pointer Device | Touchpad |
| Touchpad | Yes |
| Internal Mic | Yes |
| Speakers | 2 Speakers |
| Fingerprint Reader | Yes |
| Finger Print Sensor | No |
Ports and slots
| Number of USB Ports | 4 |
| USB Ports | 2 x USB 2.0, 1 x USB 3.1 Gen 1 (Type A), 1 x USB 3.1 Gen 1 (Type C) |
| HDMI Port | Standard |
| Multi Card Slot | 1 Micro SD Card Reader |
| Headphone and Mic Combo Jack | Yes |
Comments
Post a Comment